Using IoT to Plastics Management
Introduction
Plastics are one of the most widely used materials in the world today. They are versatile, durable, and inexpensive, making them popular in a wide range of industries. The global plastic market is expected to reach USD 722.6 billion by 2027, with an annual growth rate of 3.4%. This growth is attributed to the increasing demand for plastic products in various applications such as packaging, construction, automotive, and electronics.
Advantages of plastics
Plastics have many advantages as a material, which is why they have become so prevalent in modern society. One of the most significant advantages is their versatility. Plastics can be molded into any shape or size, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. They are also lightweight, which makes them easy to transport and handle.
Plastics are an essential material with many applications at the macro- and micro-economic level. They help to solve a multitude of problems that society has had to face throughout history. They are used as lightweight and innovative materials in the automotive industry, where they help to save fuel and reduce CO2 emissions. They have a high performance when used as insulators, so they contribute to achieve considerable energy savings. They are widely used as packaging, where they ensure food safety and reduce food waste. In recent years, they have even been combined with 3D printing technology for the manufacture of biocompatible medical parts that can save human lives.
Another advantage of plastics is their durability. Plastics can withstand extreme temperatures, chemicals, and weather conditions, making them suitable for use in harsh environments. They are also resistant to impact, which makes them ideal for use in packaging and transportation.
Finally, plastics are relatively inexpensive to produce, which makes them an attractive option for manufacturers. This low cost allows for the production of large quantities of products at a low price point.
Inconvenients of plastics
Despite the many advantages of plastics, they also have some significant drawbacks. One of the most significant is their potential to release harmful chemicals. Plastics are made from petroleum-based materials, which can contain toxic chemicals such as bisphenol A (BPA) and phthalates. These chemicals can leach into food, water, and other substances, which can have harmful effects on human health. In addition, the production of plastics requires a significant amount of energy and resources, which can contribute to climate change and other environmental problems.
But what may be the biggest issue with plastics is related to its waste management. Plastics are not biodegradable, which means they can persist in the environment for hundreds of years. This persistence leads to significant problems such as plastic pollution, which can harm wildlife, ecosystems, and human health. The problems caused by plastic waste and the current situation of the sector make it necessary to rethink processes and business models to ensure the sustainability of the sector. The need to develop a circular economy in the plastics industry and the actions this entails have already been identified in the literature, together with analyses of how these needs might be met through the use of technologies and enablers of Industry 4.0.
This recently published article aims the preliminary design of a plastic waste management network that integrates the technologies and concepts of Industry 4.0 and the principles of the circular economy. For this purpose, the Industrial Internet Reference Architecture (IIRA) methodology has been used to cover all stages of the life cycle of plastic products. A model combining the use of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies to optimize plastic waste management is presented as a sustainable technological and economical alternative with the potential to improve environmental, social and corporate governance for greater sustainability of the plastics industry.
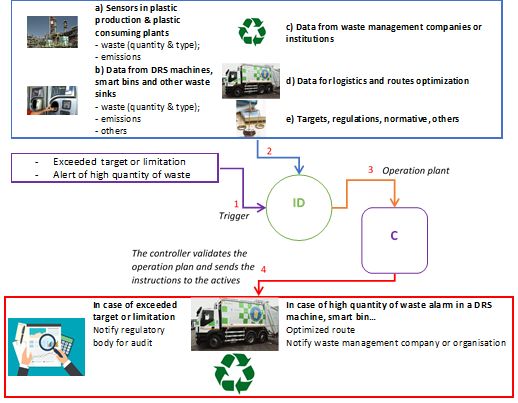
The holistic methodology adopted enables the development of a versatile, adaptable and scalable architecture that will be of interest to public and private actors in the plastics value chain.
The article is a result of my final project for the master’s degree in Industry 4.0 at the International University of La Rioja and it has been developed together with the Dr. Daniel María González Pérez & Dr. J. Javier Rainer.
Conclusions
Plastics have become an integral part of modern society due to their versatility, durability, and low cost. However, their widespread use has also led to significant environmental and health problems. It is essential to reduce the consumption of single-use plastics, promote recycling, and rethink the strategy when using plastic as a material. By doing so, we can reduce the impact of plastics on the environment and create a more sustainable future for generations to come.